Chandkheda, Ahmedabad, Gujarat
- GST NO. : 24CJWPK9058H1ZI
| Business Type | Exporter, Supplier |
| Application | To treat malaria |
| Shelf Life | 36 Months |
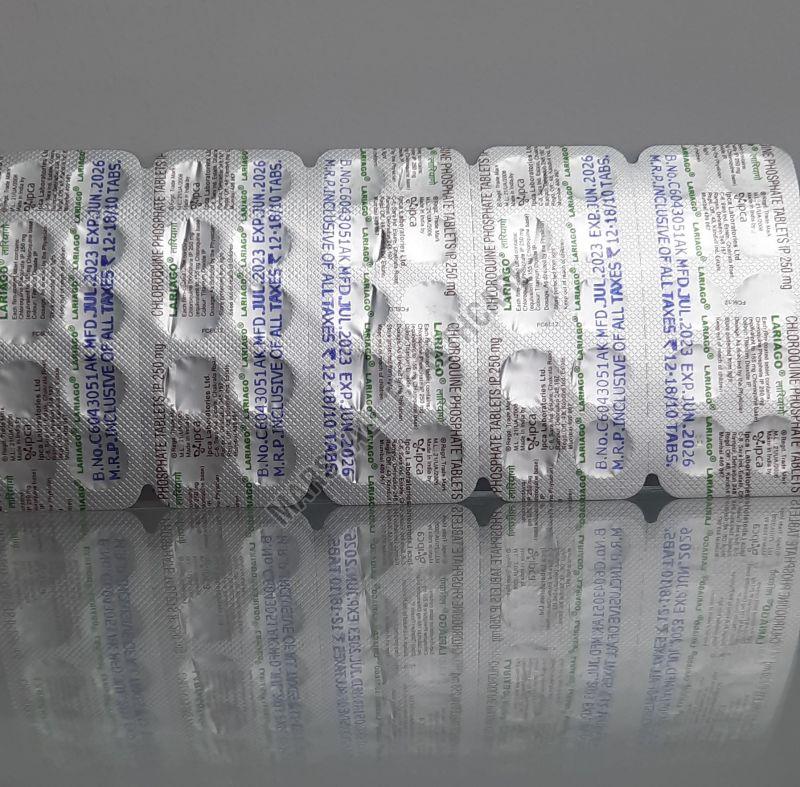
| Strength | chloroquine 250 mg Tablet |
| Click to view more | |
Product Details
Chloroquine is an oral medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials. It is used to prevent and treat malaria and also has been used for other conditions like extraintestinal amebiasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus.
Physical Description
-
Form: Tablet for oral administration.
-
Appearance: White to slightly yellow, odorless, crystalline powder. The tablets themselves can be white or coated in other colors, such as pink.
-
Taste: Bitter.
Uses
Chloroquine is primarily used for:
-
Malaria:
-
Prevention (Prophylaxis): Used to prevent malaria in areas where the parasites are known to be sensitive to chloroquine.
-
Treatment: Used to treat acute, uncomplicated malaria caused by specific strains of parasites (e.g., P. vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale, and susceptible P. falciparum).
-
-
Extraintestinal Amebiasis: A liver infection caused by a protozoan parasite.
-
Other (Off-label or historical uses): Chloroquine and its derivative, hydroxychloroquine, have been used in the past for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of chloroquine depends on the condition being treated, the patient's weight, and whether it's for prevention or treatment. It is often prescribed as a phosphate salt, and the dosage is sometimes expressed in terms of the chloroquine base.
-
Prevention of Malaria: Typically taken once a week on the same day, starting 1-2 weeks before traveling to an endemic area, during the stay, and for four weeks after leaving.
-
Treatment of Malaria: A higher initial dose is followed by smaller doses over the next several days.
-
Extraintestinal Amebiasis: A high dose for the first two days, followed by a lower dose for several weeks.
It is crucial to follow a doctor's instructions for dosage and duration.
Side Effects
Common side effects of chloroquine are often mild and include:
-
Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain)
-
Headache
-
Dizziness
-
Pruritus (itching)
More serious, though less common, side effects can occur, especially with high doses or long-term use. These include:
-
Ocular Toxicity: Irreversible retinal damage leading to vision problems or loss. This is a significant concern with prolonged use.
-
Cardiovascular Issues: Heart rhythm problems (e.g., QT prolongation, ventricular fibrillation) and cardiomyopathy.
-
Neurological Effects: Seizures, paranoia, and hallucinations.
-
Blood Disorders: Hemolytic anemia, especially in individuals with a genetic condition called G6PD deficiency.
Contraindications and Precautions
Chloroquine should not be used in patients with:
-
Hypersensitivity: A known allergy to chloroquine or other 4-aminoquinoline compounds.
-
Pre-existing Retinal or Visual Field Changes: The drug can worsen these conditions and cause irreversible vision damage.
It should be used with caution in patients with a history of:
-
Heart disease or heart rhythm problems
-
Liver or kidney disease
-
Psoriasis
-
Epilepsy
Looking for "Chloroquine Phosphate Tablets" ?
Explore More Products